Updated 26 March 2025 at 17:18 IST
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope Captures Stunning Auroras on Neptune
Auroras are natural light displays that occur when energetic particles from the Sun are trapped by a planet’s magnetic field.
- Science News
- 2 min read
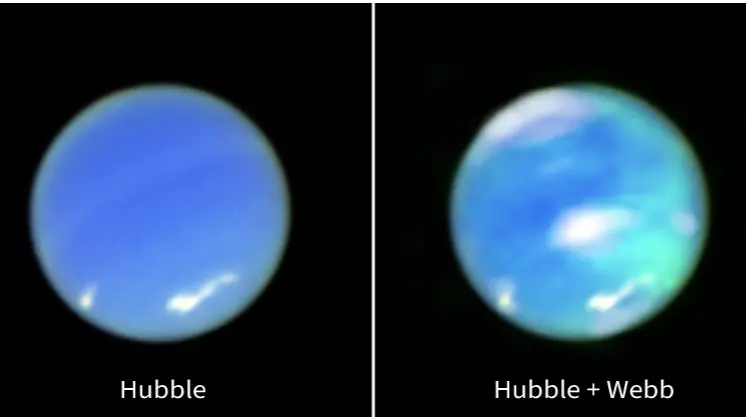
New Delhi: NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has captured bright auroral activity on Neptune, a planet that had long eluded astronomers regarding aurora imaging. This marks a significant milestone in understanding the dynamic atmosphere of the ice giant, as auroras on other gas giants like Jupiter, Saturn, and Uranus had been observed before.

What Are Auroras?
Auroras are natural light displays that occur when energetic particles from the Sun are trapped by a planet’s magnetic field and collide with its upper atmosphere. These collisions release energy in the form of glowing light, creating the signature auroral phenomenon.

Previous Attempts to Spot Neptune’s Auroras
Although hints of auroral activity were spotted during NASA's Voyager 2 flyby of Neptune in 1989, capturing clear images has remained a challenge. While auroras were detected on other gas giants, Neptune’s elusive auroras remained a mystery until the JWST’s recent observation in June 2023.
Webb’s Technology Unveils New Details
The breakthrough discovery was made possible by the Webb telescope’s advanced near-infrared sensitivity.
Advertisement
Henrik Melin, a lead researcher from Northumbria University, expressed his amazement at the clarity and detail of the auroral images, stating that the findings “shocked” him.
In addition to capturing the auroras, the team used Webb’s Near-Infrared Spectrograph to gather data about Neptune’s upper atmosphere, or ionosphere.
Advertisement

The observations revealed the presence of a unique emission line linked to the trihydrogen cation (H3+), a key indicator of auroral activity.
Neptune’s Auroras: A Unique Discovery
Unlike Earth, Jupiter, and Saturn, where auroras are typically confined to the poles, Neptune’s auroras were found at its mid-latitudes. This is due to the planet’s unusual magnetic field, which is tilted 47 degrees from its rotational axis. As a result, auroras occur in different regions, further challenging astronomers' understanding of the planet's magnetic behavior.
Uncovering the Mysteries of Neptune’s Atmosphere
In addition to revealing the auroras, the Webb data also provided insight into the temperature of Neptune’s upper atmosphere. The results show that Neptune’s atmosphere has cooled dramatically since the Voyager 2 mission in 1989. The current temperature is now much lower, which may explain why the auroras remained hidden for so long.
Published By : Isha Bhandari
Published On: 26 March 2025 at 17:17 IST
